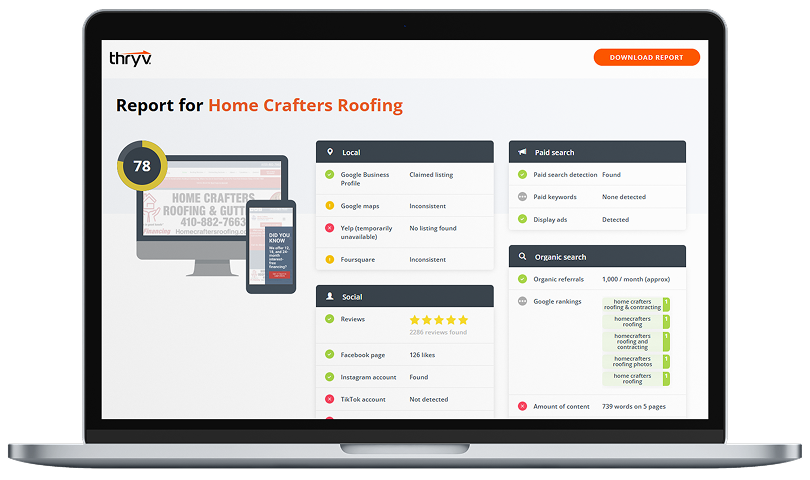
With the everchanging landscape of SEO the past couple of years, business owners must now know more than the seven essential seo terms we published back in 2012. Google has gone through major iterations of how they calculate and rank websites, and that has caused SEO “experts” to redefine their new selling tactics. Knowing what terms mean and how they apply to SEO on your website can save you much headache and heartache down the road.
- Algorithm: An algorithm is just a process or set of instructions to be followed in calculations or problem-solving in an automated fashion. In the SEO world, “The Algorithm” usually refers to the complex set of rules and calculations used by search engine Google, to attach a value to websites and individual web pages. The ongoing study and research to understand this algorithm is the basis of SEO. What you, as business owners, need to know is that no one outside of the engineers at Google actually know what this algorithm is comprised of. Many SEOs have good ideas and theories about how it runs, but if anyone tells you they can guarantee anything against it, you need to walk away.
- Panda: Google is constantly tweaking the way their algorithm works. Major updates to it usually get tagged with a codename. In this case, “Panda” was a major algorithm change at Google. Many changes to the algorithm are based on trying to combat the “black-hat” SEOs and web spammers. Panda was introduced to the algorithm as a way to measure “quality content”. What that means is Google is checking websites for content that is thin (very little content on a page), scraped (content stolen from somewhere else), duplicate (multiple pages on the site presenting the same information); or content that does not belong in the website’s overall category, function and purpose (for example, articles about dating on a site selling car parts). The purpose of Panda is to check for content quality, so the next time an SEO company, digital marketing company, etc. talks about the Panda effect or the Panda update, you will have an idea of what they are talking about.
- Penguin: Like Panda, Penguin is another major addition to Google’s algorithm. Penguin’s function, however is completely different in nature. While Panda checks for all things content, Penguin checks a website’s backlinks and for abnormalities or gaming of the algorithm. Since the inception of Google’s search engine, links have always played a very important part in their determination of which sites should rank higher than other sites. As time went on, people began to catch on to that fact, and started to game the system by creating, buying, and sharing links. Back in those days, the more links a website had, the more the algorithm valued that site and ranked it higher. As people doing SEO became more and more aware of this “tactic”, they started to stuff the internet with backlinks (see #4) whether they were relevant to their site or not. Buying links became a big business, and soon spammy sites started to outrank more legitimate sites just because they had many more backlinks. This was a big problem for Google whose stated mission is to serve users the most relevant search results possible. Hence, the Penguin update. It evaluates links for relevancy and penalizes sites that are using and buying into “link schemes” (see #5).
- Backlinks: Backlinks are links FROM other websites TO your website. Theoretically, each link is an indication that your site and content are relevant enough for another website to trust it and therefore link to it. This is equivalent to a digital form of “word-of-mouth” in the real world. The more people talk about you, the more authoritative you should be. This word-of-mouth method was the basis of Google’s algorithm and, to some extent, still plays a large part in how they value your website. It is, however, more scrutinized for relevancy now because of how black-hat SEOs and spammers were using it to boost their websites. What you should know is that even in this time of Penguin, your backlinks are still a significant factor in how Google determines the importance of your website to the niche it serves. The algorithm still values relevant and legitimate backlinks from other authoritative sites as one of the most important factors for ranking. You should be leery of people contacting you, “advising” you that you should be getting rid of, or disavowing (see#6) your links.
- Link Schemes: As Google puts it, “any links intended to manipulate PageRank or a site’s ranking in Google search results may be considered part of a link scheme and a violation of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.” These links can be identified by Google’s algorithm (Penguin in particular) as unnatural and spammy, meaning they are not relevant to the subject matter of that website or they only exist to add value to the site producing the link. Link schemes can include forum signature links; comments on blogs that have links pointing back to the target site; foreign links; links on blogs that exist primarily to create backlinks, etc. These schemes leave identifiable “footprints” that can usually be sniffed out by Google, which will and has penalized sites (removed them completely from search results) for this activity. While these link schemes can produce a quick boost to a website initially, they are never sustainable and the offending website will be penalized. So if you have hired anyone to do “SEO” on your website, it would be beneficial for you to check your own backlinks to see if there are any risky linking activities before your site becomes penalized.
- Disavow: You can’t control which websites link to yours, and there may be sites linking to you that you’d rather not have associated with your site. Disavow is a tool that Google has made available to webmasters and website owners to “disavow” or tell Google that some of the backlinks pointing to their website should not count towards their ranking. This is a powerful tool, and should be used with caution. Often it can do more damage than good, because using it properly requires research and a good understanding of which backlinks might actually be bad and which are beneficial. This has now become a popular sales tactic for “shady” SEO agencies. The same guys who used to sell links that got websites in trouble in the first place have now shifted to using scare tactics of Penguin and Panda to sell “link removal” services. As a business owner, you should be hesitant if anyone recommends that you purge your backlinks without giving a very specific reason to do so along with thorough research of your backlinks to evaluate each of them.
As algorithms get updated, it is essential for business owners who want a viable online presence to maintain a good understanding of what is new and what has changed. This knowledge will allow you understand what services you are buying and why.